

The reaction is followed either by a release or absorption of energy. The energy-producing mechanism in a fusion reactor is the joining together of two light atomic nuclei. If this radioactivity were to escape the reactor, its impact on the people in the vicinity would be severe. These reactors require a moderator to reduce the speed of neutrons produced by fission. Nuclear reactors contain very large amounts of radioactive isotopesmostly fission products but also such heavy elements as plutonium. Thermal reactors use slow neutrons to maintain the reaction. For details about reactor types, see nuclear reactor: Nuclear fission reactors. All of the reactor types require a coolant to remove the heat generated water, a gas, or a liquid metal may be used for this purpose, depending on the design needs. Nuclear fusion is the joining of two nuclei to form a heavier nuclei. The speed of the neutrons in the chain reaction determines the reactor type (Figure 7.13. In a fast reactor, fast fission neutrons maintain the chain reaction, and no moderator is needed. Both fission and fusion can be used as an energy source, but fission is the only one thats used in modern nuclear power plants. "We want to have a head-start once the technology will break through.\( \newcommand\ J\). Examples of nuclear fission The splitting of uranium-235 nuclei when hit by a neutron, which results in the release of energy and two or three new nuclei. “This is a technology with much perspective for large scale energy production," the NRG's Sander de Groot said, according to Thorium Energy World. However, while there have been significant development in fusion research, it might still take a while before it can be stabilized enough for expanded use. Nuclear fusion is still potentially the safest and most powerful energy source humankind can harness - capable of generating four times as much energy as fission.

With many countries now more keen than ever to pursue cleaner alternative sources of energy, there's a renewed interest in thorium-based fission.
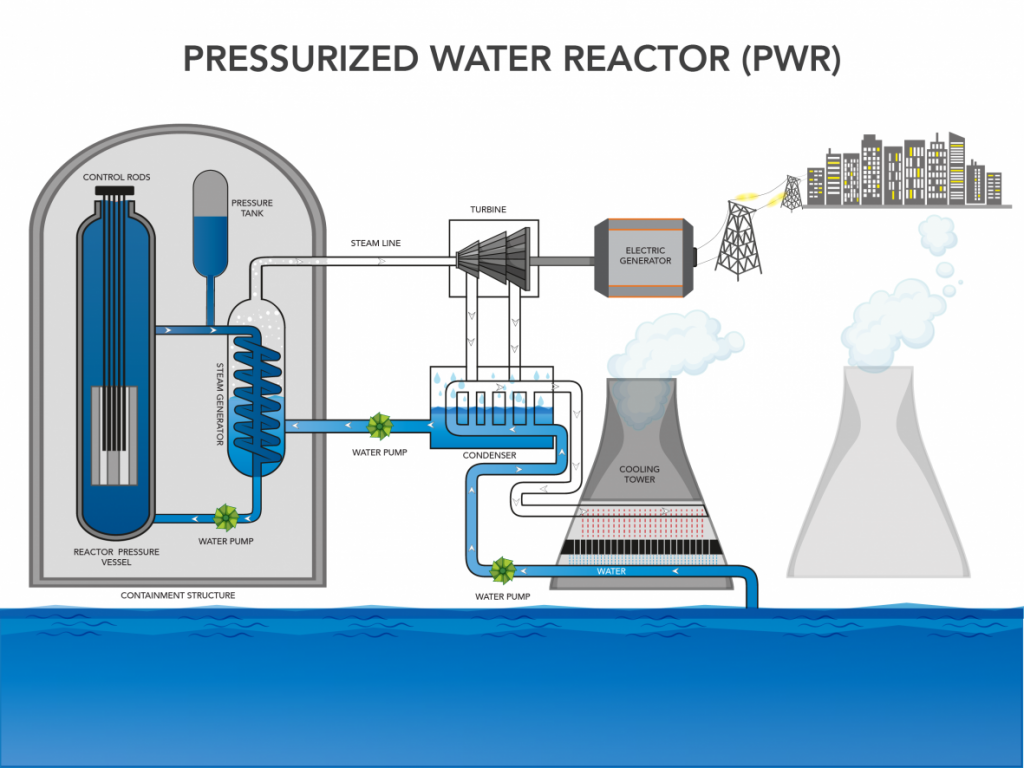
It's also possible to use thorium in a liquid form, and reactor designs built around this could essentially be self-regulating and fail-safe. This could, at least in theory, consume used nuclear fuel from ordinary uranium-based fission reactors. The pressurized water reactor is the most common type of nuclear reactor. The NGR's program begins by testing several small-scale reactor designs, where its first experiment uses a setup called a molten-salt fast reactor that burns thorium salts. There are two basic types: the pressurized water reactor and the boiling water reactor. As a result, unlike other energy sources, nuclear power plants do not release carbon or. To get this kind of nuclear reaction to work, thorium is made to absorb neutrons that convert it to an artificial uranium isotope. Instead, they split uranium atoms in a process called fission. It's designed to protect itself against meltdown, and it's also not as easy to weaponize like uranium. Nuclear reactors are used as research tools, as systems for producing radioactive isotope s, and most prominently as energy sources for nuclear power plants.

#NUCLEAR FISSION REACTOR TYPES SERIES#
A thorium-salt reactor, which is a type of molten-salt reactor, promises a safer kind of nuclear power. nuclear reactor, any of a class of devices that can initiate and control a self-sustaining series of nuclear fission s. Nuclear reactors use the energy released by the splitting of atoms (nuclear fission) or the merging of atoms (nuclear fusion) to produce heat, which is then used to create steam that drives a turbine and produces electricity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
